Room setup
SubZone calculates the best position for your subwoofer by simulating the acoustics of your room. To do this accurately, you will need to provide the following information about your room:
- Dimensions (width, length and height)
- Construction materials
Add a room
When you first use SubZone, you will be automatically presented with the Add room screen (see right). Subsequently, you can add more rooms by pressing the ‘+’ button in the bottom-right of the Rooms screen.
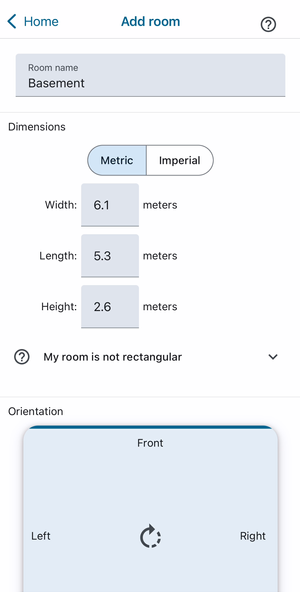
Room name
Give the room a name - you can call it whatever you like 🙂
Dimensions
Enter the width, length, and height of your room. The accuracy of the results will depend on these measurements, so we suggest you measure the room yourself using a tape measure or laser distance measure, rather than trying to guess.
We suggest you measure to within 10cm, or 4 inches, of the actual room dimensions for the best results. If your walls are not entirely flat, measure the distance between the two biggest surface areas of each wall.
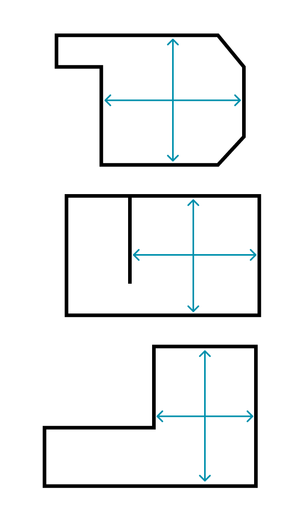
Non-rectangular rooms
SubZone is designed to simulate closed rectangular spaces, as this can be run on a phone. Although we currently can’t simulate more complex spaces accurately, you may still be able to place your subwoofer using the following tips and example diagrams.
Broadly speaking, you should enter the distance between the largest opposing flat surfaces. These produce the room modes that have the largest effect on the result.
If your room is broken into more that one area, such as by a wall or a corner, measure the area of the room that is used as the listening space
If your ceiling is partly sloped, ignore the slope and measure to the flat part. The sloped part will not produce room modes that are as strong.
We have included some example floor plans below, showing where we suggest you measure.
Orientation
Set the orientation of your room by selecting whether the front wall is shorter or longer than the side walls. You can change the orientation by pressing the rotate button in the middle of the map.
Construction materials
The materials used to construct your room affect its acoustic absorption, which in turn affect the size of various room modes. To model the acoustics of your room, we need to estimate the acoustic absorption of your walls, ceiling, and floor. We have made this as simple as possible by producing a list of the most common construction materials for you to choose from.

As we’re dealing with bass frequencies, we’re only interested in what materials your room is constructed from (e.g. brick), rather than what materials are on the surface (e.g. plaster), as the surface materials don’t have much effect on low-frequency absorption.
If you’re unsure about your room’s construction materials, knock on your wall/ceiling/floor. Uninsulated stud walls/joists will sound hollow; insulated stud walls/joists will make a dull thud; and brick/concrete will make very little sound.
If you can’t find a suitable material to choose from, or you’re really not sure what the room is constructed of, you can select the “Other / not sure” option. This will use an average of typical rooms.
When you’re finished, press the ‘next’ button to add a listening position.